Scan Tech Surveys
When It Comes to Solutions!
Scan Tech Surveys
When It Comes to Solutions!
3D Scanning of a Large Fitness Complex Utilising TLS and SLAM Scanner
In our recent project we have applied Terresterial Laser Scanner and Slam handheld Scanner to complete 3D Scan of the entire ROAR fitness centre located in Bibra Lake (Western Australia). We have conducted 650 individual scans with TLS and over 3,000 sqm with Slam. These two datasets have been combined accurately to suit the needs of the project. The main objective of the project was re-desgin the internal spaces and renovatoin. In this case the role of 3D Scanning data is vital.
In the realm of architectural and engineering marvels, capturing precise measurements and detailed 3D models of large buildings has traditionally been a meticulous and time-consuming task. However, with advancements in technology, particularly in the field of 3D laser scanning, this process has been revolutionized, offering efficient solutions that combine accuracy with flexibility.
Terrestrial 3D Laser Scanners: Capturing Monuments of Precision
Terrestrial 3D laser scanners are formidable tools designed for capturing large-scale environments with utmost precision. These scanners operate on a stationary platform and utilize laser beams to map the surroundings in intricate detail. By rotating and capturing data from multiple angles, they create a comprehensive point cloud, which serves as the foundation for detailed 3D models. This method is ideal for capturing exterior facades, vast interiors, and complex architectural features of buildings, making it indispensable in fields such as urban planning, historical preservation, and construction.
Handheld SLAM Scanners: Flexibility Meets Detail
In contrast, handheld SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) scanners offer unparalleled flexibility and mobility. These devices employ advanced algorithms to track their own position in real-time while mapping the environment. This allows them to capture intricate details in hard-to-reach areas, such as narrow corridors, intricate staircases, and areas with limited accessibility. Handheld SLAM scanners are particularly useful for capturing interior spaces where maneuverability and close-range precision are paramount.
Advantages and Applications
Both terrestrial and handheld SLAM scanners have distinct advantages:
- Terrestrial Scanners excel in capturing large-scale exteriors and interiors with high accuracy and detail.
- Handheld SLAM Scanners offer flexibility and accessibility, enabling detailed scans of confined or complex spaces.
These scanners find applications across various industries:
- Architecture and Construction: Facilitating accurate as-built documentation and planning.
- Engineering: Supporting structural analysis and retrofitting projects.
The Future of 3D Laser Scanning
As technology continues to evolve, the future of 3D laser scanning holds promise for even greater precision, speed, and accessibility. Enhanced integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM) systems and artificial intelligence will further streamline workflows and enhance the utility of scanned data in design and construction phases.
In conclusion, whether employing a terrestrial scanner for capturing monumental exteriors or a handheld SLAM scanner for intricate interiors, 3D laser scanning stands at the forefront of modern technology, revolutionizing how we document, analyze, and preserve our built environment. Its ability to combine precision with versatility makes it an indispensable tool in the arsenal of architects, engineers, and preservationists alike.
Exploring 3D Laser Scanning: Terrestrial vs. Handheld SLAM Scanners
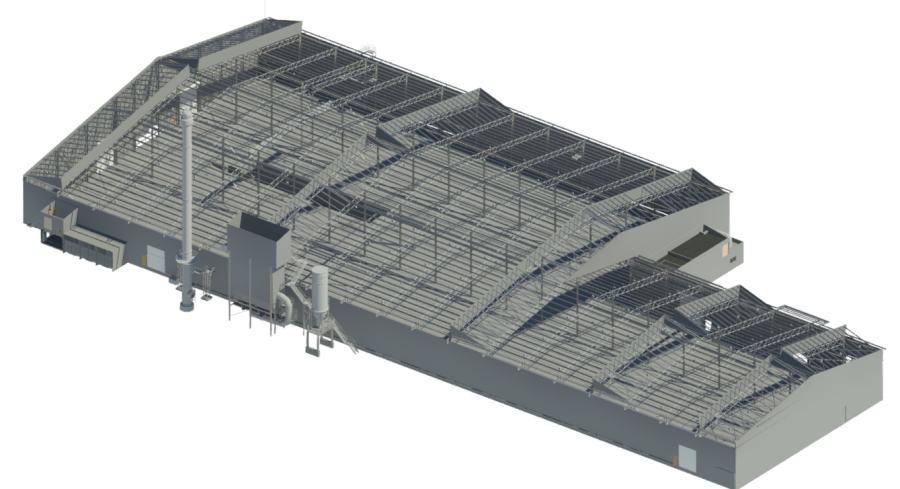
Large Scale Steel Structure 3D Scan and 3D Model
3D laser scanning, also known as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), is a powerful technology increasingly used in structural surveying. This method involves using laser beams to measure distances and create precise, three-dimensional models of structures and their environments.
By following this structured workflow and adhering to best practices, you can successfully convert point cloud data from a large warehouse scan into an accurate and detailed 3D solid model. This solid model can then be used for various purposes, such as renovation planning, structural analysis, or archival documentation.
Transforming the intricate point cloud data from a 3D laser scan of a large warehouse into a precise 3D solid model unlocks new dimensions of accuracy and insight, revolutionizing the way we approach structural design.
Using 3D laser scanning technology for scanning boat hulls offers numerous benefits for various stakeholders involved in boat design, construction, maintenance, and repair. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Precision and Accuracy: 3D laser scanning provides highly accurate measurements of the boat hull's geometry. This precision is crucial for ensuring that any modifications or repairs are executed accurately and fit seamlessly with the existing structure.
-
Time Efficiency: Compared to traditional methods of manually measuring boat hulls, 3D laser scanning is significantly faster. It captures detailed data of the entire hull quickly, reducing the time needed for measurement and assessment.
-
Comprehensive Data Capture: Laser scanning technology captures a comprehensive dataset of the boat hull, including intricate details and complex geometries that might be challenging to measure accurately using traditional methods.
-
Non-contact Scanning: Laser scanning is a non-contact method, which means it does not require physical contact with the boat hull. This reduces the risk of damage to the vessel during the scanning process, making it particularly suitable for delicate or sensitive hulls.
-
Improved Design and Modification: The detailed 3D models generated from laser scanning allow designers and engineers to assess the hull's structure more effectively. It enables them to make informed decisions regarding design modifications, improvements, or repairs.
-
Digital Documentation: Laser scanning produces digital replicas of boat hulls, providing valuable documentation for future reference. This digital data can be archived and used for various purposes, such as historical preservation, design analysis, or insurance documentation.
-
Reverse Engineering: Laser scanning facilitates reverse engineering processes by creating accurate digital models of existing boat hulls. This is useful for replicating or modifying hull designs, particularly in the context of restoration projects or custom boat building.
-
Quality Control: Laser scanning technology enables thorough quality control assessments of boat hulls during construction or maintenance. By comparing scanned data to design specifications, manufacturers can identify and rectify any deviations or defects promptly.
-
Cost Savings: While the initial investment in laser scanning equipment and software may be significant, the efficiency and accuracy it offers can lead to long-term cost savings. By reducing errors, rework, and downtime, boat builders and operators can minimize expenses associated with design flaws or maintenance issues.
-
Safety: Laser scanning can be performed from a safe distance, minimizing the need for personnel to work in potentially hazardous environments such as confined spaces or underwater. This enhances safety for workers involved in hull inspection and maintenance operations.
Overall, the adoption of 3D laser scanning technology for scanning boat hulls offers a range of benefits, including improved accuracy, efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness throughout the entire lifecycle of a vessel.
Sample: https://scantechsurveys.com.au/Potree_1.8/Gallery/Boat/Boat.html
The adoption of 3D laser scanning technology for scanning boat hulls offers a range of benefits, including improved accuracy, efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness throughout the entire lifecycle of a vessel.
Using 3D laser scanning for the as-built documentation of rail culverts
3D laser scanning for the as-built documentation of rail culverts offers several benefits:
Accuracy: 3D laser scanning provides highly accurate measurements and detailed representations of the rail culvert's geometry, capturing even the smallest details with precision. This accuracy ensures that the as-built documentation reflects the true condition of the structure, reducing the risk of errors and discrepancies.
Efficiency: Compared to traditional surveying methods, 3D laser scanning is much faster and more efficient. The scanning process can be completed in a fraction of the time it would take to manually measure and record data, allowing for rapid data acquisition and processing.
Comprehensive Data Capture: Laser scanning captures millions of data points to create a detailed point cloud of the rail culvert and its surroundings. This comprehensive data capture enables engineers and designers to analyze the structure from various angles and perspectives, facilitating better decision-making and problem-solving.
Minimized Disruption: Since 3D laser scanning is non-contact and non-destructive, it minimizes disruption to rail operations and surrounding environments. Scanning can often be performed without the need for track closures or extensive site preparation, reducing downtime and costs associated with surveying activities.
Safety: Laser scanning allows for remote data collection, keeping surveyors out of potentially hazardous environments such as busy rail corridors or unstable terrain. This improves safety for surveying personnel and reduces the risk of accidents or injuries on-site.
Documentation and Visualization: 3D laser scanning generates detailed digital models and visualizations of the rail culvert, which can be easily shared and accessed by project stakeholders. These digital assets serve as valuable documentation for future reference, maintenance planning, and asset management.
Sample: https://scantechsurveys.com.au/Potree_1.8/Gallery/RTIO-CULVERTS/DD180344/DD180344.html
Overall, leveraging 3D laser scanning for the as-built documentation of rail culverts enhances efficiency, accuracy, and safety while providing comprehensive data capture and documentation for infrastructure management and maintenance purposes.
We use state-of-the-art Technologies, fitting the scope of the job to save time and increase efficiency and Safety
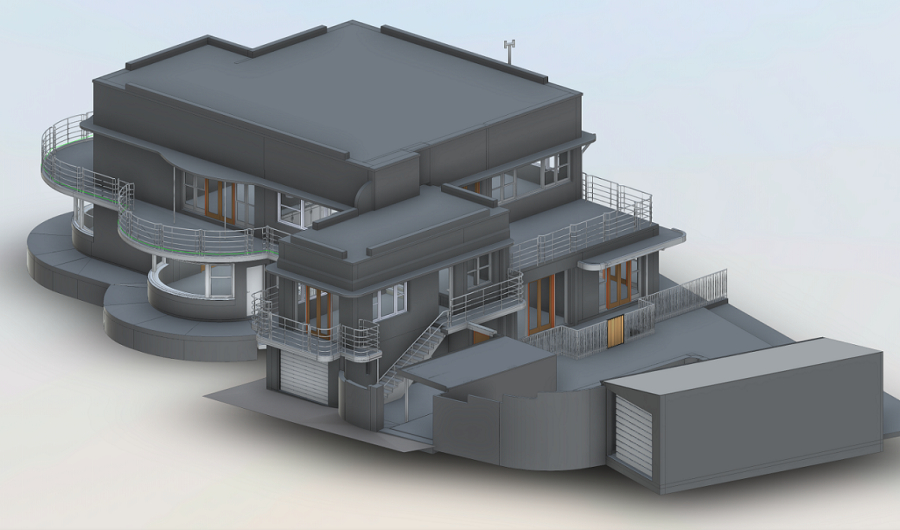
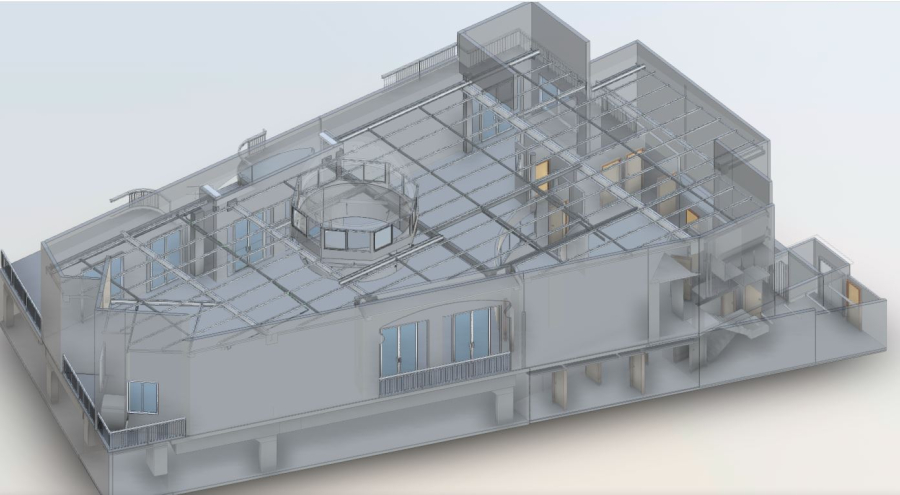
3D Scan of a Residential Building
3D Scan to BIM (Building Information Modeling) is a process that involves converting point cloud data obtained from 3D laser scanning into a detailed and accurate digital representation of a building or infrastructure. This process is particularly useful in architecture, engineering, and construction industries for renovation, retrofitting, and maintenance projects.
Here is a general overview of the steps involved in the 3D Scan to BIM process:
-
3D Laser Scanning:
- Use a 3D laser scanner to capture accurate and detailed point cloud data of the existing building or structure.
- The scanner emits laser beams and measures the time it takes for the laser to return, creating a point cloud that represents the surfaces and geometry of the scanned environment.
-
Data Cleanup and Filtering:
- Remove any unwanted or extraneous data points from the point cloud.
- Filter out noise or errors introduced during the scanning process.
-
BIM Modeling:
- Import the 3D mesh into BIM software (such as Revit)
- Create intelligent BIM elements such as walls, floors, ceilings, doors, windows, and other architectural and structural components based on the scanned data.
-
Quality Control:
- Verify the accuracy of the BIM model by comparing it to the original point cloud data.
- Make adjustments as needed to ensure the model aligns with the actual physical structure.
The 3D Scan to BIM process significantly improves the efficiency and accuracy of building documentation and design in construction and architectural projects. It allows for better decision-making, clash detection, and collaboration among stakeholders.
3D Scanning for Deflection Report
A well-structured and comprehensive 3D laser scanning report for structural deflection should provide a clear understanding of the structure's condition, the extent of any movement, and any necessary actions for maintenance or improvement. We have completed two epochs of 3D scans for determining the deflection of K frames of shading cloth sheets of a swimming pool. The deflection was due to the expansion and retraction of the shading sheets and the tension forced from connecting cables. The results provided a thorough dimensional report to the client for each span.
We use state-of-the-art Technologies, fitting the scope of the job to save time and increase efficiency
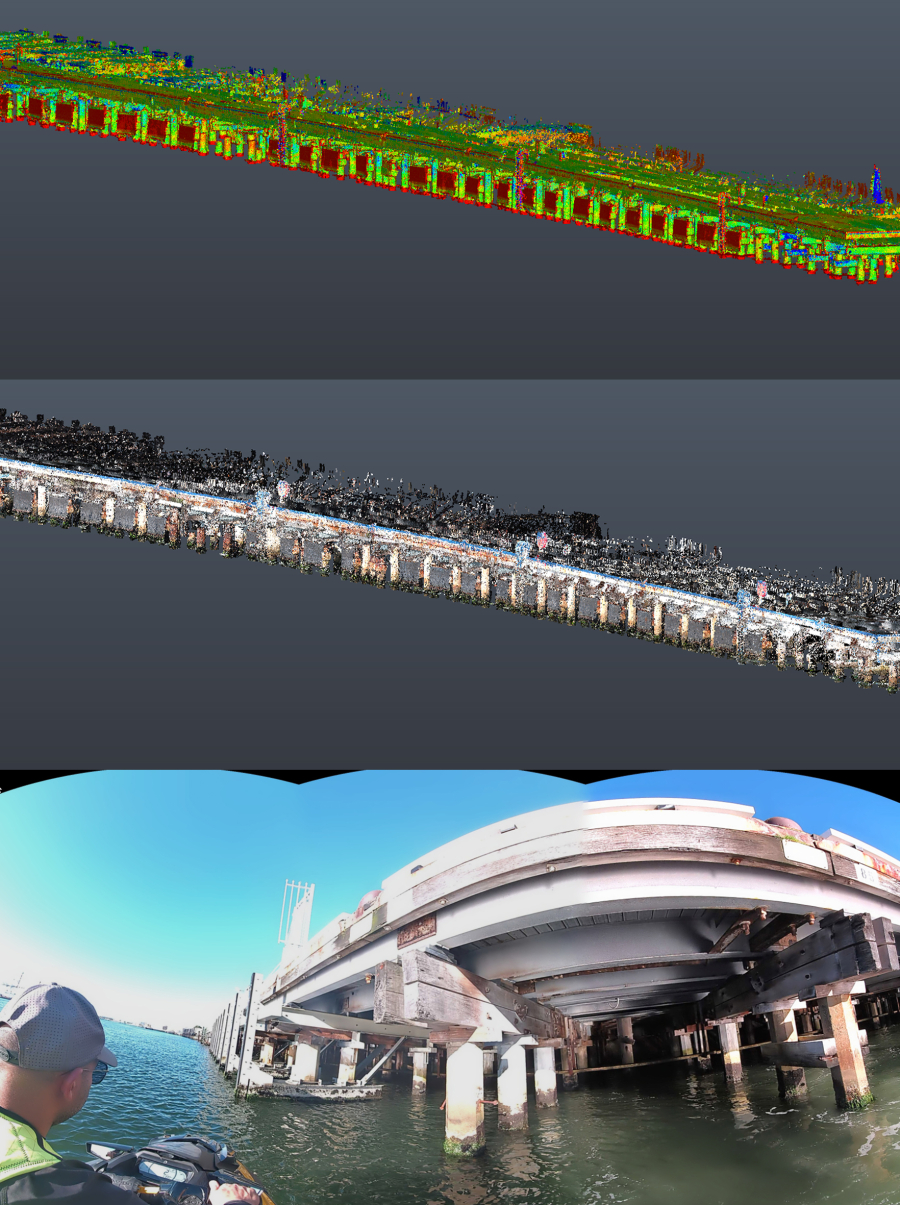
3D Scanning of the Pillars of a Wharf
Our Slam Scanner is now equipped with RTK module which is a significant factor in controlling drift when doing corridor mapping without the need to make loops in the capture path. The RTK module eliminates the need for GCPs for horizontal orientation.
Recently we completed a 3D scan of the underside pillars of a Wharf; 3D Scanning operation was done from the waterside on a JetSki while RTK module was connected to our Ntrip Base network via the in-built GSM modem. The trajectory of the scanner has been captured within 1-2 cm accuracy and there was no drift as expected.
We use state-of-the-art Technologies, fitting the scope of the job to save time and increase efficiency
Slab Flatness Analysis
Slab flatness analysis using 3D laser scanning is a precise and efficient method for evaluating the flatness and levelness of large horizontal surfaces such as concrete slabs, road pavements, airport runways, warehouse floors, and more. This technology provides highly accurate and detailed data about the surface geometry, which can be crucial for quality control, maintenance, and construction projects.
In our recent project, SCAN TECH SURVEYS was tasked to prepare a heatmap report about the rise and fall values on a warehouse slab with 2-3 mm accuracy. We used our top-of-the-range Scan Station P50 Scanner to compile this comprehensive report.
We have expertise and experience to create high quality and comprehensive reports for levelness and flatness of conceret slabs
Slam Mobile Scanner
A SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) handheld scanner with RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) positioning combines the capabilities of SLAM technology with highly accurate real-time positioning. This combination offers several benefits in various applications:
High Precision Mapping: RTK positioning provides centimeter-level accuracy in real-time. When combined with SLAM, it enables the creation of extremely precise 3D maps of environments. This is especially useful in applications like construction, archaeology, and forestry, where accurate mapping is critical.
- Efficient Surveying: Surveyors and land professionals can use SLAM handheld scanners with RTK to significantly reduce surveying time and effort. The high accuracy of RTK ensures that survey data is reliable, while SLAM technology helps automate the mapping process, making it more efficient.
- Indoor and GPS-Denied Environments: Traditional GPS systems may not work well indoors or in environments with limited GPS signal availability (e.g., dense urban areas or forests). SLAM with RTK allows for precise mapping and positioning in such GPS-denied scenarios, making it valuable for indoor navigation, construction within buildings, or forest management.
- Improved Augmented Reality: When used in augmented reality (AR) applications, the combination of SLAM and RTK allows for more accurate and stable AR overlays. This can enhance user experiences in gaming, navigation, or industrial training scenarios.
- Autonomous Robotics: SLAM with RTK is crucial for autonomous robots, drones, and vehicles operating in dynamic, unstructured environments. The high precision of RTK positioning combined with SLAM's mapping capabilities enables safe and efficient navigation, making these technologies suitable for agriculture, search and rescue, and autonomous vehicles.
- Reduced Drift and Error: RTK helps mitigate drift and cumulative error in the SLAM system. Over time, SLAM systems can accumulate errors in position estimation, especially in large environments. RTK positioning provides corrections that keep the SLAM map aligned with the real-world environment.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Management: SLAM handheld scanners with RTK positioning can be invaluable in emergency response and disaster management. They can quickly create accurate maps of disaster-stricken areas, aiding rescue teams in their efforts to locate victims and plan rescue operations.
- Infrastructure Inspection: Infrastructure inspection, such as power lines, pipelines, and bridges, can benefit from the high accuracy of RTK positioning when combined with SLAM. It allows for precise monitoring, maintenance planning, and anomaly detection.
- Reduced Manual Intervention: With RTK-enhanced SLAM, there is less reliance on manual measurements and positioning, reducing the risk of human error and speeding up data collection and analysis processes.
- Cost Savings: While RTK-equipped devices and SLAM technology can be an investment, the increased efficiency, accuracy, and reduced need for manual labor can lead to significant cost savings in various industries over the long term.
Overall, the combination of SLAM handheld scanners with RTK positioning offers enhanced accuracy and efficiency across a wide range of applications, making it a valuable tool for professionals in fields such as surveying, construction, robotics, and emergency response.
"Unlock a new dimension of accuracy and productivity with the Slam RTK handheld scanner, revolutionizing spatial data capture.
3D Scan of Roof Steel Structure
In the field of architecture, engineering, and construction, technology continues to revolutionize the way we approach various challenges. One such innovative technique gaining traction is 3D scanning of roof structures. This method offers numerous benefits, from accurate measurements to streamlined renovation projects. In this blog post, we will delve into the advantages of 3D scanning for roof structures and shed light on the scanning process.
Advantages of 3D Scanning for Roof Structures
-
Accurate Measurements: Traditional methods of measuring roof structures can often be time-consuming and prone to human errors. 3D scanning eliminates these issues by providing precise measurements of the entire roof with minimal human intervention. This accuracy is particularly important when planning renovations or designing new structures that need to align perfectly with existing roofs.
-
Time and Cost Efficiency: 3D scanning drastically reduces the time required for data collection compared to traditional methods. This efficiency translates into cost savings since fewer man-hours are needed for the scanning process. Moreover, the collected data can be shared digitally with architects, engineers, and other stakeholders, reducing the need for multiple site visits.
-
Enhanced Safety: Roof inspections can be hazardous, requiring workers to climb to considerable heights. 3D scanning eliminates the need for prolonged physical presence on the roof, thus reducing the risk of accidents. This is especially beneficial when assessing roofs with complex geometries or in challenging weather conditions.
-
Comprehensive Data Capture: Traditional methods might miss intricate details of a roof's structure. 3D scanning captures comprehensive data, including the exact shape, dimensions, and surface irregularities. This data can be valuable for conducting structural analyses and simulations.
-
Better Project Visualization: With a detailed 3D model of the roof, architects and clients can visualize how different design elements will interact with the existing structure. This enhances decision-making and ensures that the final design aligns with the initial vision.
3D scanning of roof structures is revolutionizing the way we approach construction and renovation projects