Scan Tech Surveys
When It Comes to Solutions!
Scan Tech Surveys
When It Comes to Solutions!
Scan to BIM
3D Scan of a Residential Building
3D Scan to BIM (Building Information Modeling) is a process that involves converting point cloud data obtained from 3D laser scanning into a detailed and accurate digital representation of a building or infrastructure. This process is particularly useful in architecture, engineering, and construction industries for renovation, retrofitting, and maintenance projects.
Here is a general overview of the steps involved in the 3D Scan to BIM process:
-
3D Laser Scanning:
- Use a 3D laser scanner to capture accurate and detailed point cloud data of the existing building or structure.
- The scanner emits laser beams and measures the time it takes for the laser to return, creating a point cloud that represents the surfaces and geometry of the scanned environment.
-
Data Cleanup and Filtering:
- Remove any unwanted or extraneous data points from the point cloud.
- Filter out noise or errors introduced during the scanning process.
-
BIM Modeling:
- Import the 3D mesh into BIM software (such as Revit)
- Create intelligent BIM elements such as walls, floors, ceilings, doors, windows, and other architectural and structural components based on the scanned data.
-
Quality Control:
- Verify the accuracy of the BIM model by comparing it to the original point cloud data.
- Make adjustments as needed to ensure the model aligns with the actual physical structure.
The 3D Scan to BIM process significantly improves the efficiency and accuracy of building documentation and design in construction and architectural projects. It allows for better decision-making, clash detection, and collaboration among stakeholders.
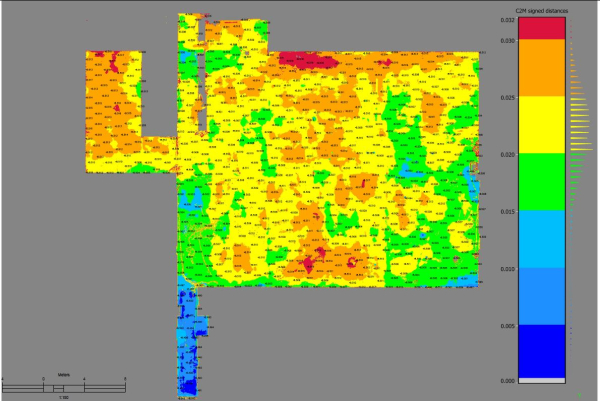
Slab Flatness Analysis
Slab Flatness Analysis
Slab flatness analysis using 3D laser scanning is a precise and efficient method for evaluating the flatness and levelness of large horizontal surfaces such as concrete slabs, road pavements, airport runways, warehouse floors, and more. This technology provides highly accurate and detailed data about the surface geometry, which can be crucial for quality control, maintenance, and construction projects.
In our recent project, SCAN TECH SURVEYS was tasked to prepare a heatmap report about the rise and fall values on a warehouse slab with 2-3 mm accuracy. We used our top-of-the-range Scan Station P50 Scanner to compile this comprehensive report.
We have expertise and experience to create high quality and comprehensive reports for levelness and flatness of conceret slabs